Black Hand (Serbia) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Unification or Death ( sr, Ujedinjenje ili smrt, italics=yes, sr-Cyrl, Уједињење или смрт), popularly known as the Black Hand ( sr, Crna ruka, italics=yes, links=no, sr-Cyrl, Црна рука), was a secret military society formed in 1901 by officers in the
 In August 1901, a group of lower officers headed by captain
In August 1901, a group of lower officers headed by captain
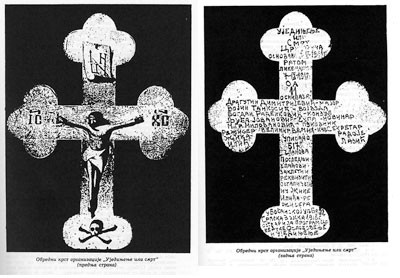
 Unification or Death was established at the beginning of May 1911, and the original constitution of the organization was signed on 9 May. Ljuba Čupa, Bogdan Radenković, and
Unification or Death was established at the beginning of May 1911, and the original constitution of the organization was signed on 9 May. Ljuba Čupa, Bogdan Radenković, and
"The Serbian 'Black Hand',"
''The Freeman'', Vol. 7, N°. 164, pp. 179–81, 2 May 1923. * John Paul Newman
Black Hand
in
{{Authority control Serbian revolutionary organizations History of Austria-Hungary Kingdom of Serbia Serbia in World War I Ottoman Empire in World War I Causes of World War I Serbian nationalism Christian fundamentalism Secret societies in Serbia Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria Serbian irredentism History of the Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina History of the Serbs of Croatia 1901 establishments in Serbia Political history of Serbia Organizations established in 1901 Defunct organizations based in Serbia Austria-Hungary–Serbia relations Vardar Macedonia (1918–1941) Revolutionary organizations against the Ottoman Empire Revolutionary organizations against Austria-Hungary Yugoslavism Freemasonry-related controversies
Army of the Kingdom of Serbia
The Army of the Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Војска Краљевине Србије, Vojska Kraljevine Srbije), known in English as the Royal Serbian Army, was the army of the Kingdom of Serbia that existed between 1882 and 1918, succeedi ...
. It gained a reputation for its alleged involvement in the assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria, (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914) was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.
F ...
in Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see Names of European cities in different languages (Q–T)#S, names in other languages'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its a ...
in 1914 and for the earlier assassination of the Serbian royal couple in 1903, under the aegis of Captain Dragutin Dimitrijević
Dragutin Dimitrijević ( sr-Cyrl, Драгутин Димитријевић; 17 August 1876 – 24 June 1917), better known by his nickname Apis, was a Serbian army officer and chief of the military intelligence section of the general staff in ...
( "Apis").
The society formed to unite all of the territories with a South Slavic majority not then ruled by either Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
or Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. It took inspiration primarily from the unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century Political movement, political and social movement that resulted in the Merger (politics), consolidation of List of historic stat ...
in 1859–1870 but also from the unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federalism, federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with ad ...
in 1871. Through its connections to the June 1914 assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria, (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914) was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.
F ...
in Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see Names of European cities in different languages (Q–T)#S, names in other languages'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its a ...
, carried out by the members of the youth movement Young Bosnia
Young Bosnia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Mlada Bosna, Млада Босна) was a separatist and revolutionary movement active in the Condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austria-Hungary before World War I. Its members were predominantly ...
, the Black Hand is often viewed as instrumental in starting World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–1918) by precipitating the July Crisis of 1914
The July Crisis was a series of interrelated diplomatic and military escalations among the major powers of Europe in the summer of 1914, Causes of World War I, which led to the outbreak of World War I (1914–1918). The crisis began on 28 June 1 ...
, which eventually led to Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
's invasion
An invasion is a Offensive (military), military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitics, geopolitical Legal entity, entity aggressively enter territory (country subdivision), territory owned by another such entity, gen ...
of the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
in August 1914.
Background
Apis' conspiracy group and the May Coup
 In August 1901, a group of lower officers headed by captain
In August 1901, a group of lower officers headed by captain Dragutin Dimitrijević
Dragutin Dimitrijević ( sr-Cyrl, Драгутин Димитријевић; 17 August 1876 – 24 June 1917), better known by his nickname Apis, was a Serbian army officer and chief of the military intelligence section of the general staff in ...
"Apis" established a conspiracy group (called the Black Hand in literature), against the dynasty. The first meeting was held on 6 September 1901. In attendance were captains Radomir Aranđelović, Milan F. Petrović, and Dragutin Dimitrijević
Dragutin Dimitrijević ( sr-Cyrl, Драгутин Димитријевић; 17 August 1876 – 24 June 1917), better known by his nickname Apis, was a Serbian army officer and chief of the military intelligence section of the general staff in ...
, as well as lieutenants Antonije Antić Antonije is a Serbian language, Serbian given name. Notable people with this name include the following:
*Antonije Abramović (1919–1996), Montenegrin Eastern Orthodox priest
*Antonije Bagaš (fl. 1366 – 1385), Serbian nobleman
*Antonije Isakov ...
, Dragutin Dulić, Milan Marinković, and Nikodije Popović. They made a plan to kill the royal couple— King Alexander I Obrenović and Queen Draga
Queen or QUEEN may refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a Kingdom
** List of queens regnant
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Queen mother, a queen dowager who is the mothe ...
. On the night of 28/29 May 1903, Captain Apis personally led a group of Army officers who murdered the royal couple at the Old Palace in Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
(Old Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, this is the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries between 158 ...
). Along with the royal couple, the conspirators killed Prime Minister Dimitrije Cincar-Marković
Dimitrije Cincar-Marković ( Šabac, 6 September 1849 – Belgrade, 11 June 1903) was a Serbian politician serving as the Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Serbia, army general, Chief of General Staff, professor of war history and strategy.
As o ...
, Minister of the Army Milovan Pavlović Milovan ( sr-Cyrl, Милован) is a Slavic name derived from the passive adjective ''milovati'' ("caress"). It is recorded in Serbia since the Late Middle Ages. Variants include Milovanac and Milovanče.
Given name
* Milovan Bojić (born 1955), ...
, and General-Adjutant Lazar Petrović
Lazar Petrović (10 March 1855 – 11 June 1903) was a Serbian general, adjutant of King Aleksandar Obrenović and professor at Belgrade Military Academy.
Early life
Petrović was born in Bašino Selo in Macedonia. Early in his life his fam ...
. This became known as the May Coup.
Narodna Odbrana
On 8 October 1908, just two days after Austria annexed Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbian ministers, officials, and generals held a meeting at the City Hall in Belgrade. They founded a semi-secret society, the ''Narodna Odbrana
Narodna Odbrana ( sr-cyr, Народна одбрана, literally, "The People's Defence" or "National Defence") was a Serbian nationalist organization established on October 8, 1908 as a reaction to the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and ...
'' ("National Defense") which gave Pan-Serbism
The term Greater Serbia or Great Serbia ( sr, Велика Србија, Velika Srbija) describes the Serbian nationalist and irredentist ideology of the creation of a Serb state which would incorporate all regions of traditional significance to ...
a focus and an organization. The purpose of the group was to liberate Serbs under the Austro-Hungarian occupation. They also shared anti-Austrian propaganda and organized spies and saboteurs to operate within the occupied provinces. Satellite groups were formed in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
, Bosnia, Herzegovina, and Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
. The Bosnian group became deeply associated with local groups of pan-Serb activists such as ''Mlada Bosna'' ("Young Bosnia
Young Bosnia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Mlada Bosna, Млада Босна) was a separatist and revolutionary movement active in the Condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austria-Hungary before World War I. Its members were predominantly ...
").
Establishment

 Unification or Death was established at the beginning of May 1911, and the original constitution of the organization was signed on 9 May. Ljuba Čupa, Bogdan Radenković, and
Unification or Death was established at the beginning of May 1911, and the original constitution of the organization was signed on 9 May. Ljuba Čupa, Bogdan Radenković, and Vojislav Tankosić
Vojislav Tankosić ( sr-cyr, Војислав Танкосић, 20 September 1880 – 2 November 1915) was a Serbian military officer, ''vojvoda'' of the Serbian Chetnik Organization, major of the Serbian Army, and member of the Black Hand, who ...
wrote the constitution of the organization, modeled after similar German secret nationalist associations and the Italian Carbonari
The Carbonari () was an informal network of secret revolutionary societies active in Italy from about 1800 to 1831. The Italian Carbonari may have further influenced other revolutionary groups in France, Portugal, Spain, Brazil, Uruguay and Ru ...
. The organization was mentioned in the Serbian parliament as the "Black Hand" in late 1911.
By 1911–12, Narodna Odbrana
Narodna Odbrana ( sr-cyr, Народна одбрана, literally, "The People's Defence" or "National Defence") was a Serbian nationalist organization established on October 8, 1908 as a reaction to the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and ...
had established ties with the Black Hand, and the two became "parallel in action and overlapping in membership".
1911–13
The organization used the magazine ''Pijemont'' (the Serbian name forPiedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, the kingdom that led the unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century Political movement, political and social movement that resulted in the Merger (politics), consolidation of List of historic stat ...
under the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of ...
) for the dissemination of their ideas. The magazine was founded by Ljuba Čupa in August 1911.
1914
By 1914, the group had hundreds of members, many of themSerbian Army
The Serbian Army ( sr-cyr, Копнена војска Србије, Kopnena vojska Srbije, lit=Serbian Land Army) is the land-based and the largest component of the Serbian Armed Forces.
History
Originally established in 1830 as the Army of Pr ...
officers. The goal of uniting Serb-inhabited territories was implemented by training guerilla fighters and saboteurs. The Black Hand was organized at the grassroots level in cells of three to five members, supervised by district committees and by a Central Committee in Belgrade, whose ten-member executive committee was primarily led by Colonel Dragutin Dimitrijević
Dragutin Dimitrijević ( sr-Cyrl, Драгутин Димитријевић; 17 August 1876 – 24 June 1917), better known by his nickname Apis, was a Serbian army officer and chief of the military intelligence section of the general staff in ...
"Apis". To ensure secrecy, members rarely knew much more than the other members of their own cell and one superior above them. New members swore the oath:
The Black Hand took over the terrorist actions of ''Narodna Odbrana
Narodna Odbrana ( sr-cyr, Народна одбрана, literally, "The People's Defence" or "National Defence") was a Serbian nationalist organization established on October 8, 1908 as a reaction to the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and ...
'' and deliberately worked
to obscure any distinctions between the two groups, trading on the prestige and network of the older organization. Black Hand members held important army and government positions. Crown Prince Alexander was an enthusiastic financial supporter. The group held influence over government appointments and policy. The Serbian government was fairly well-informed of Black Hand activities.
Friendly relations had fairly well cooled by 1914. The Black Hand was displeased with Prime Minister Nikola Pašić
Nikola Pašić ( sr-Cyrl, Никола Пашић, ; 18 December 1845 – 10 December 1926) was a Serbian and Yugoslav politician and diplomat who was a leading political figure for almost 40 years. He was the leader of the People's Radical ...
and thought that he did not act aggressively enough for the Pan-Serb cause. The Black Hand engaged in a bitter power struggle over several issues, such as who would control territories that Serbia had annexed during the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defe ...
. By then, disagreeing with the Black Hand was dangerous, as political murder was one of its tools.
In 1914, Apis allegedly decided that Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir-apparent of Austria, should be assassinated, as he was trying to pacify the Serbians, which would prevent a revolution if he was successful. Towards that end, three young Bosnian Serbs were allegedly recruited to kill the Archduke. They were certainly trained in bomb throwing and marksmanship by current and former members of the Serbian military. Gavrilo Princip
Gavrilo Princip ( sr-Cyrl, Гаврило Принцип, ; 25 July 189428 April 1918) was a Bosnian Serb student who assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria and his wife Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914.
Pr ...
, Nedeljko Čabrinović
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir presumptive to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife, Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, were assassinated on 28 June 1914 by Bosnian Serb student Gavrilo Princip. They were shot at close range while ...
, and Trifko Grabež
Trifun "Trifko" Grabež ( sr-Cyrl, Трифун Трифко Грабеж; – 21 October 1916) was a Bosnian Serb member of the Black Hand organization which was involved in the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
Early life
Trifko Gr ...
were smuggled across the border back into Bosnia by a chain of contacts similar to the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
.
The decision to kill the Archduke was initiated by Apis and not sanctioned by the full Executive Committee (if Apis was involved at all, a question that remains in disputeVladimer Dedijer, ''The Road to Sarajevo'').
Those involved probably realised that their plot would result in war between Austria and Serbia and had every reason to expect that Russia would side with Serbia. They likely did not, however, anticipate that the assassination would start the chain of events leading to World War I.
Others in the government and some of the Black Hand Executive Council were not as confident of Russian aid since Russia had recently let them down.
When word of the plot allegedly percolated through Black Hand leadership and the Serbian government (Prime Minister Pašić was informed of two armed men being smuggled across the border, but it is not clear if Pašić knew of the planned assassination), Apis was supposedly told not to proceed. He may have made a half-hearted attempt to intercept the young assassins at the border, but they had already crossed. Other sources say the attempted 'recall' began only after the assassins had reached Sarajevo. The 'recall' appears to have made Apis look like a loose cannon and the young assassins like independent zealots. The 'recall' took place fully two weeks before the Archduke's visit. The assassins idled in Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see Names of European cities in different languages (Q–T)#S, names in other languages'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its a ...
for a month. Nothing more was done to stop them.
Ideology
The group encompassed a range of ideological outlooks, from conspiratorially-minded army officers to idealistic youths, sometimes tending towards republicanism, despite their patrons in nationalistic royal circles. The movement's leader, Apis, had been instrumental in the June 1903 coup which had brought King Petar Karađorđević to the Serbian throne following 45 years of rule by the rival Obrenović dynasty. The group was denounced asnihilist
Nihilism (; ) is a philosophy, or family of views within philosophy, that rejects generally accepted or fundamental aspects of human existence, such as objective truth, knowledge, morality, values, or meaning. The term was popularized by Ivan ...
by the Austro-Hungarian press and compared to the Russian People's Will
Narodnaya Volya ( rus, Наро́дная во́ля, p=nɐˈrodnəjə ˈvolʲə, t=People's Will) was a late 19th-century revolutionary political organization in the Russian Empire which conducted assassinations of government officials in an att ...
and the Chinese Assassination Corps
The Chinese Assassination Corps (or China Assassination Corps or Sina Assassination Corps, ) was an anarchist group, active in China during the final years of the Qing dynasty. One of the first organized anarchist movements in China and fiercel ...
.
Legacy
In 1938 a conspiracy group to overthrow the Yugoslav regency was founded by, among others, members of theSerbian Cultural Club
The Serbian Cultural Club ( sr, Srpski kulturni klub, italics=yes, sr-Cyrl, Српски културни клуб; SKK) was a short-lived but influential grouping of mainly Belgrade-based Serb intellectuals of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in the yea ...
(SKK). The organization was modeled after the Black Hand, including the recruitment process. Two members of the Black Hand, Antonije Antić and Velimir Vemić, were the organization's military advisors.
See also
*Serbian Chetnik Organization
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
* Young Bosnia
Young Bosnia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Mlada Bosna, Млада Босна) was a separatist and revolutionary movement active in the Condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austria-Hungary before World War I. Its members were predominantly ...
* Serb revolutionary organizations
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * *External links
* * Lutz, Hermann"The Serbian 'Black Hand',"
''The Freeman'', Vol. 7, N°. 164, pp. 179–81, 2 May 1923. * John Paul Newman
Black Hand
in
{{Authority control Serbian revolutionary organizations History of Austria-Hungary Kingdom of Serbia Serbia in World War I Ottoman Empire in World War I Causes of World War I Serbian nationalism Christian fundamentalism Secret societies in Serbia Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria Serbian irredentism History of the Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina History of the Serbs of Croatia 1901 establishments in Serbia Political history of Serbia Organizations established in 1901 Defunct organizations based in Serbia Austria-Hungary–Serbia relations Vardar Macedonia (1918–1941) Revolutionary organizations against the Ottoman Empire Revolutionary organizations against Austria-Hungary Yugoslavism Freemasonry-related controversies